"I must study politics and war, that our sons may have liberty to study mathematics and philosophy. Our sons ought to study mathematics and philosophy, geography, natural history and naval architecture, navigation, commerce and agriculture in order to give their children a right to study painting, poetry, music, architecture, statuary, tapestry and porcelain."
- John Adams
Disseration
“The Partisan Secret: Institutional Constraints on Policy Change and Partisanship.” University of Michigan
Committee: Robert J. Franzese, Jr. (co-chair), Ted Brader (co-chair), George Tsebelis, Phoebe C. Ellsworth (Psychology)
Publication
– Winner of Deil Wright Best Paper Award (APSA Federalism and Intergovernmental Relations Section, 2014)
At the beginning of 2012, the 17 countries of the eurozone and eight of the ten remaining countries of the EU reached an agreement on the Treaty on Stability, Co-ordination, and Governance in the Economic and Monetary Union (TSCG, known as the Fiscal Compact). The article traces six successive drafts of the agreement to discover how these countries reached agreement. We argue that there are three different procedures that can lead different actors with veto power over an agreement to suspend their veto – they increase, decrease or preserve the dimensionality of the underlying space. We call the three methods compensation, elimination and compromise respectively, and discover that in the Fiscal Compact the agreement was achieved mainly through elimination.

What type of trade agreement is the public willing to accept? Instead of focusing on individual concerns about market access and trade barriers, we argue that specific treaty design and, in particular, the characteristics of the dispute settlement mechanism, play a critical role in shaping public support for trade agreements. To examine this theoretical expectation, we conduct a conjoint experiment that varies diverse treaty-design elements and estimate preferences over multiple dimensions of the Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (TTIP) based on a nationally representative sample in Germany. We find that compared to other alternatives, private arbitration, known as investor-state dispute settlement (ISDS), generates strong opposition to the trade agreement. As the single most important factor, this effect of dispute settlement characteristic is strikingly large and consistent across individuals’ key attributes, including skill levels, information, and national sentiment, among others.

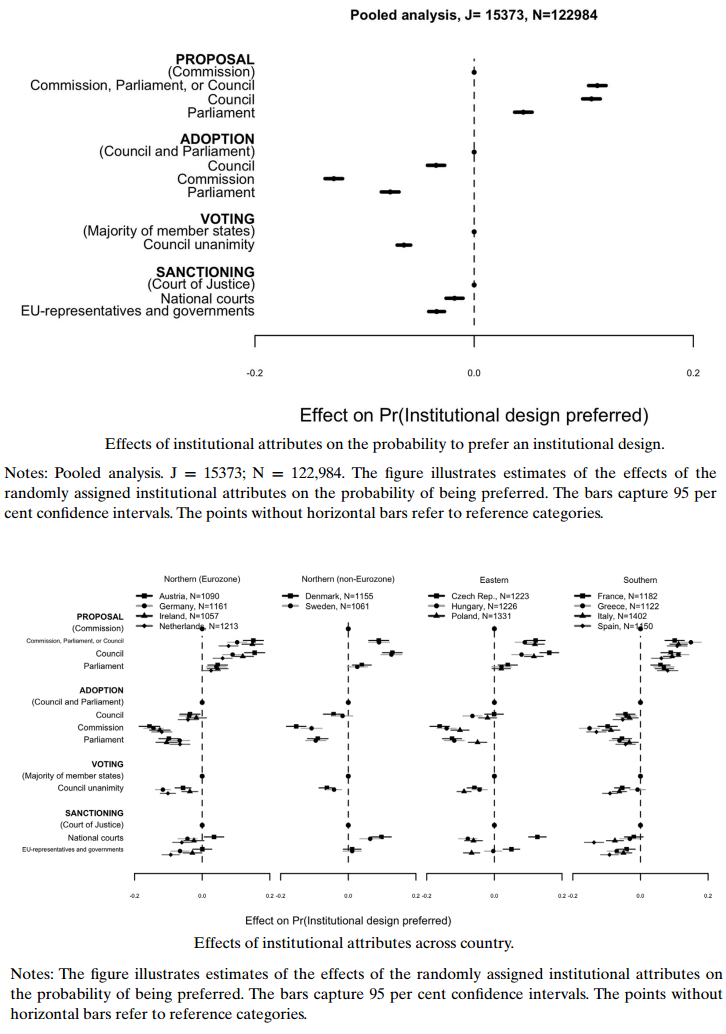
In the face of the discourse about the democratic deficit and declining public support for the European Union (EU), institutionalist scholars have examined the roles of institutions in EU decision making and in particular the implications of the empowered European Parliament. Almost in isolation from this literature, prior research on public attitudes toward the EU has largely adopted utilitarian, identity and informational accounts that focus on individual-level attributes. By combining the insights from the institutional and behavioral literature, this article reports on a novel cross-national conjoint experiment designed to investigate multidimensionality of public attitudes by taking into account the specific roles of institutions and distinct stages in EU decision making. Analyzing data from a large-scale experimental survey in 13 EU member states, the findings demonstrate how and to what extent the institutional design of EU decision making shapes public support. In particular, the study finds a general pattern of public consensus about preferred institutional reform regarding powers of proposal, adoption and voting among European citizens in different countries, but notable dissent about sanctioning powers. The results show that utilitarian and partisan considerations matter primarily for sanctioning dimension.
'최신 정치학 연구' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 함현호 외. 2023. 당파주의의 속성과 연합 파트너쉽의 역할: 유럽 사례 연구 (0) | 2022.08.12 |
|---|

댓글